Our Science
Industry-Leading Muscle Wasting Platform
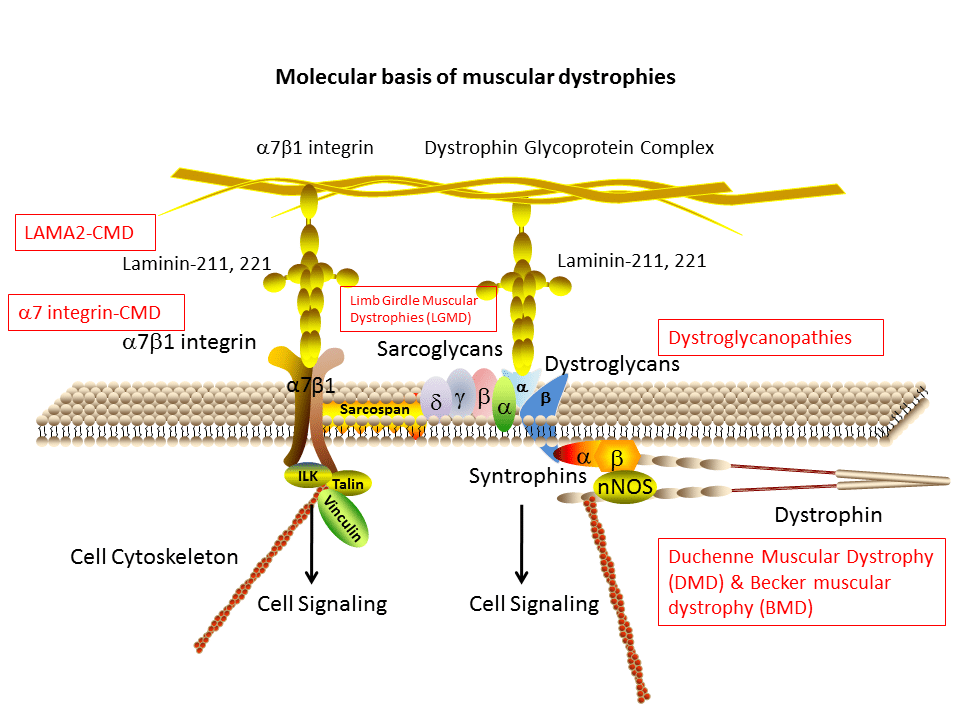
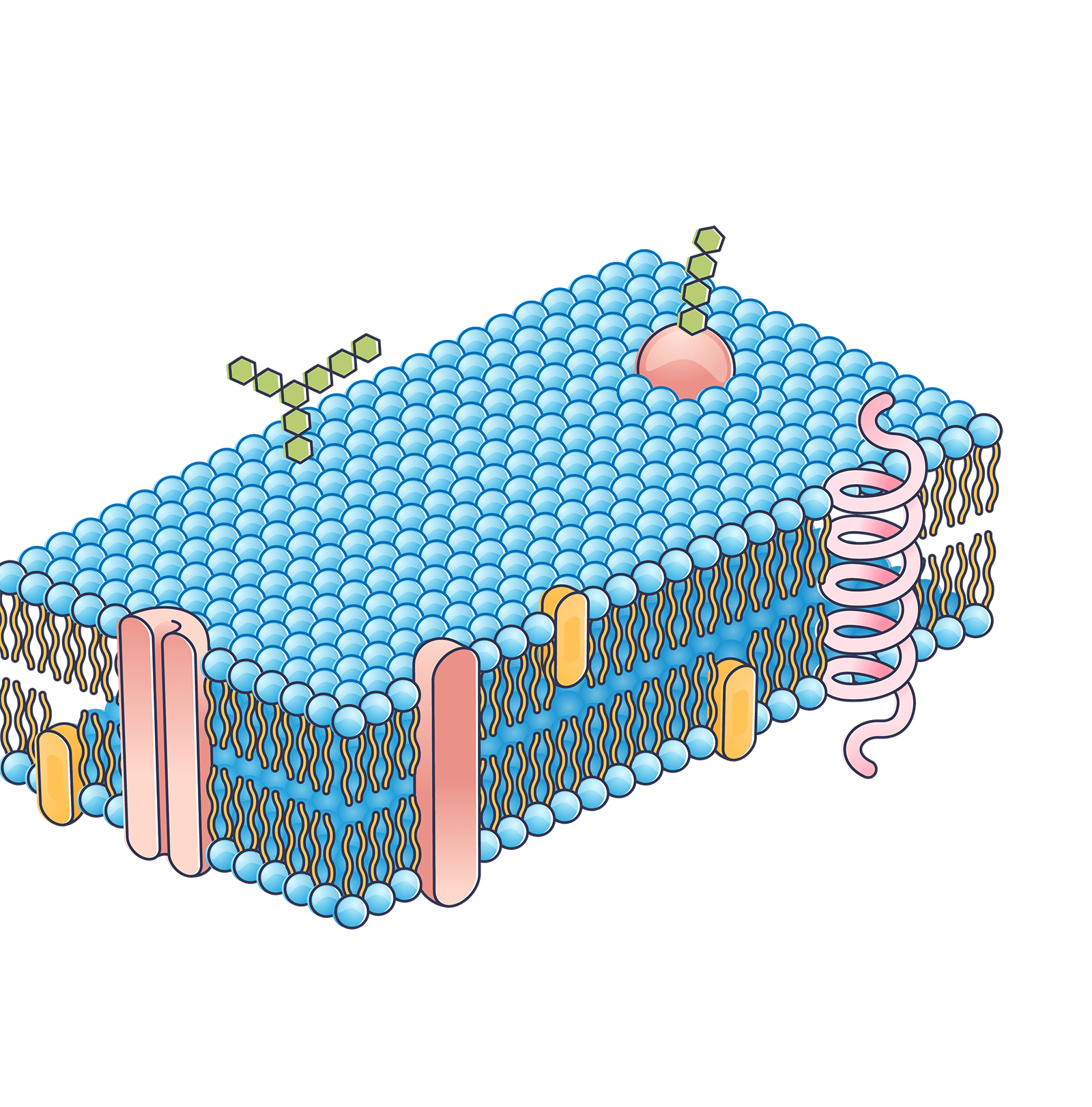
Our research is grounded in understanding the role that α7β1 integrin and laminin play in muscle development and disease. We’ve built a drug discovery platform based on a novel screening system for integrin activators and we now have a robust IP including hundreds of scaffolds supporting thousands of compounds.
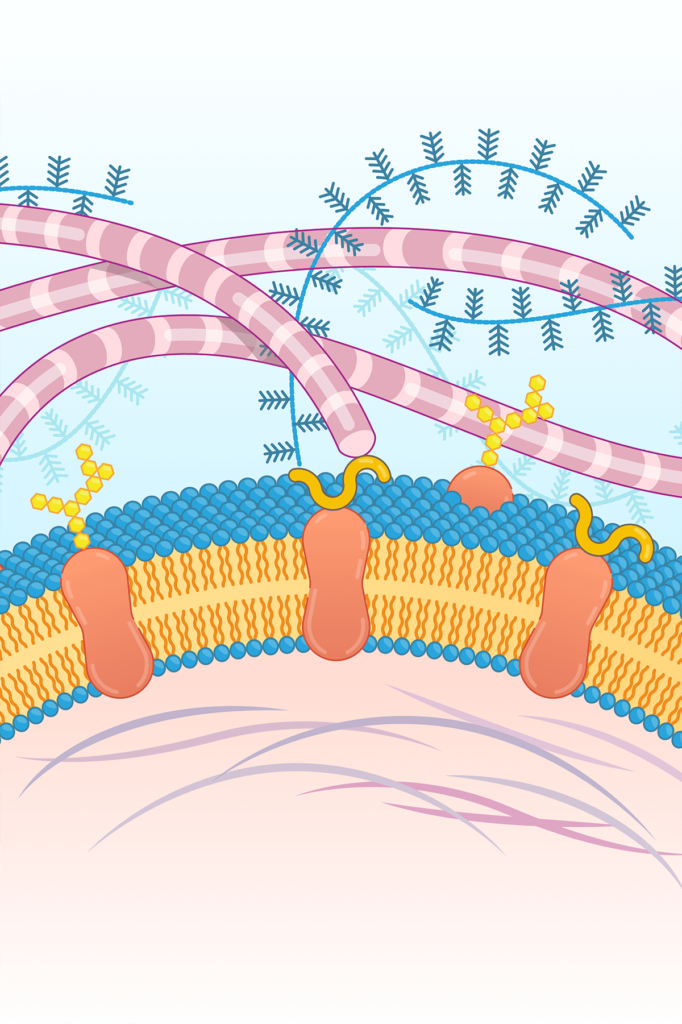
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
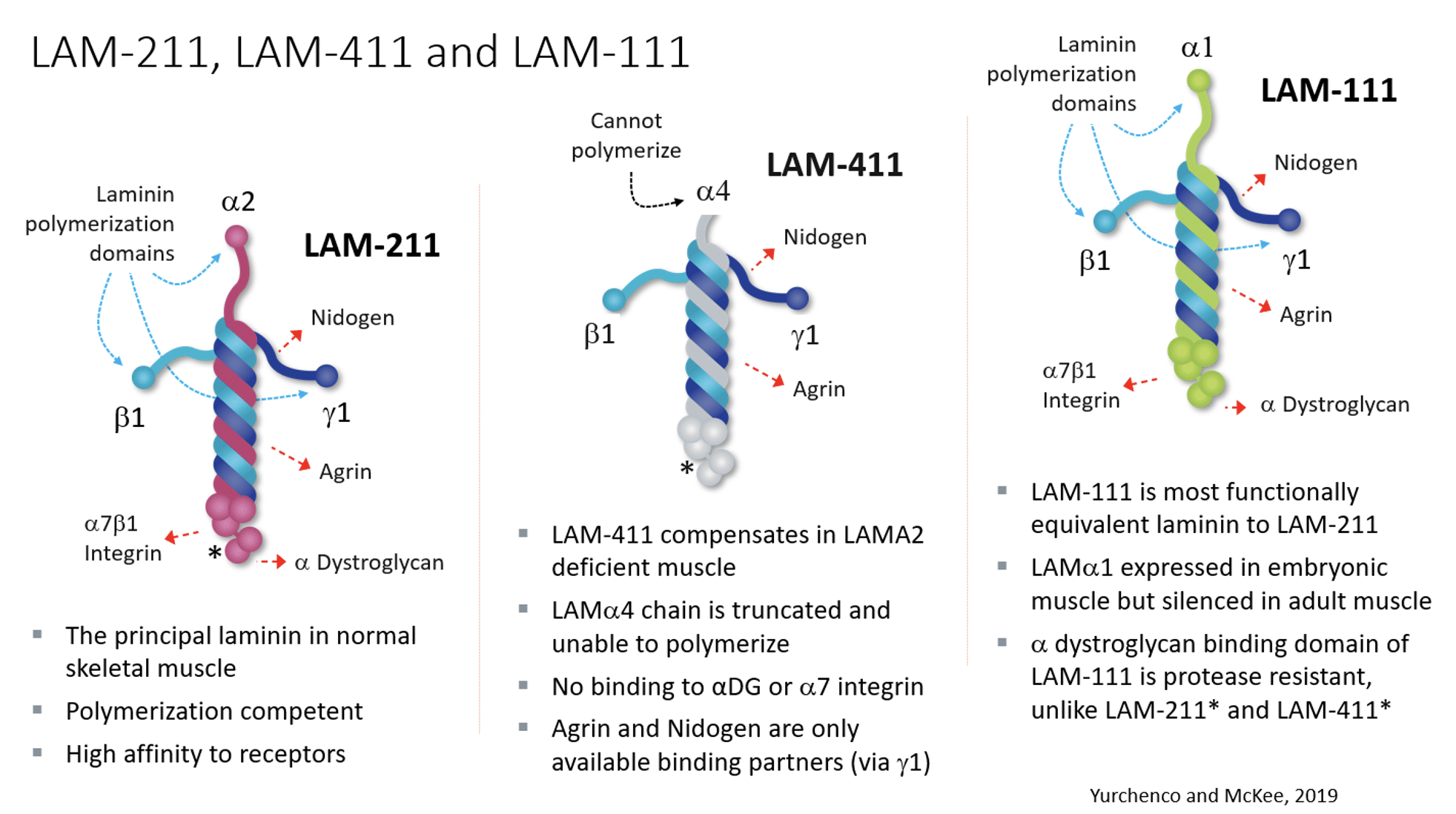
Laminin
α7β1 Integrin

S-969

Sunitinib

LAM 111

Putting It All Together
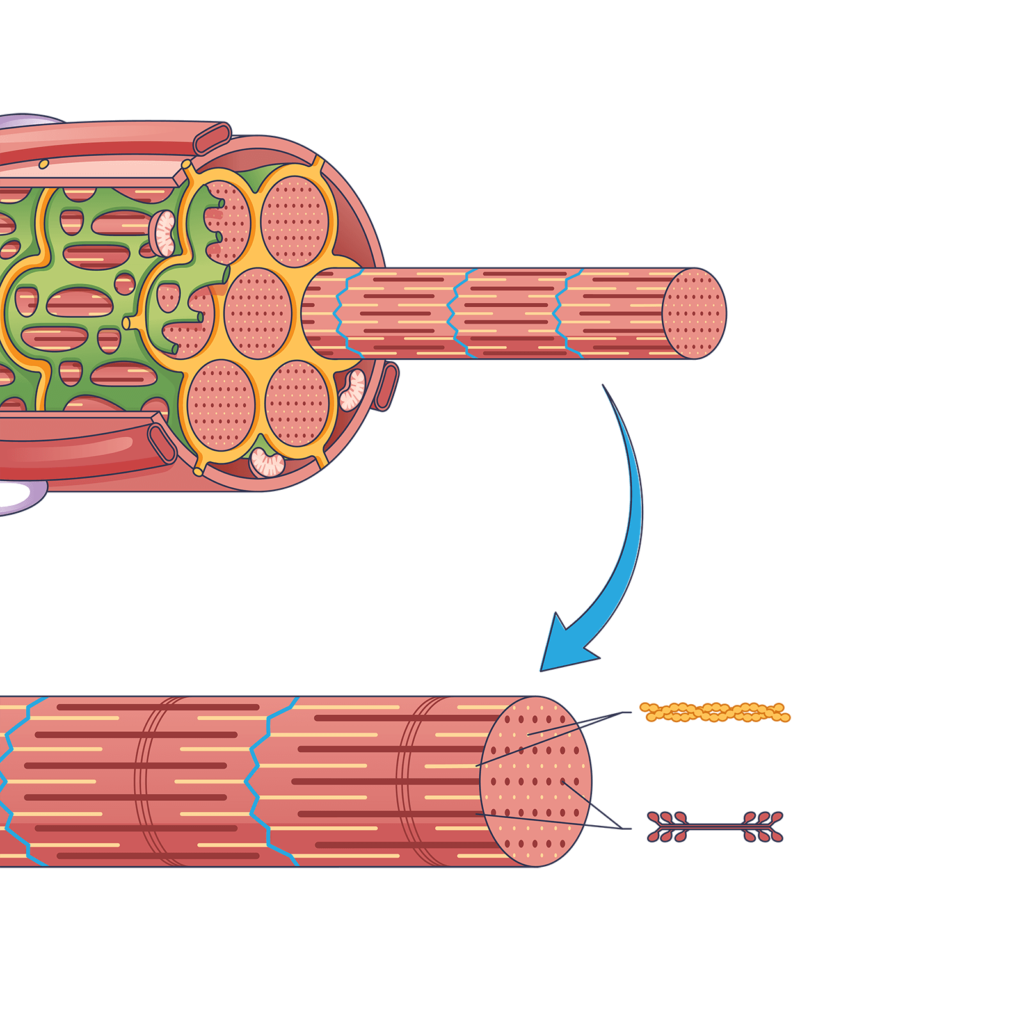
Dysregulation of α7β1 integrin and laminin function can contribute to muscle disease, including muscular dystrophy and other muscle wasting disorders. In these diseases, the normal interaction between muscle cells and the Extracellular Matrix (ECM) is disrupted, leading to muscle weakness, degeneration, and loss.
Thus, α7β1 integrin and laminin play crucial roles in muscle development and disease, and understanding their function and regulation is important for the development of therapeutic strategies for muscle disorders.